For senior engineering and technology leaders, the pace of change has never been faster. Competitive landscapes shift overnight, product delivery timelines shrink, and executives expect accurate, timely insights to back every strategic move. Today more than ever, relying on gut instinct or outdated reporting is a liability.
The competitive edge now comes from building a data-driven culture, one that allows teams to move quickly from raw data to actionable insights that directly influence execution. Recent studies show that enterprises with strong BI adoption are five times more likely to make better, faster decisions, giving them a sharp edge in high-stakes environments.
The future of business intelligence (BI) isn’t about better dashboards. It’s about truly embedding data analytics into the daily decision-making process, enabling leaders to steer the organization with clarity and confidence.
The Foundations of Modern Business Intelligence
At its core, business intelligence is a discipline that unifies data collection, data analysis, and decision-making through a structured ecosystem of tools, processes, and governance. Modern BI draws on data science, statistical algorithms, and machine learning to transform historical data into forward-looking insights.
In enterprise settings, this work starts long before the first report is generated. Data teams, including data engineers, analysts, and data scientists, manage the entire data lifecycle:
- Data collection and integration from multiple systems
- Data preparation and transformation to ensure consistent formats
- Data governance frameworks to ensure high-quality data, security, and compliance
- Ongoing monitoring to detect flawed data or incomplete data before it impacts decisions
Without strong governance and accurate data, BI systems can produce poor business decisions, often at significant cost. For leaders managing multimillion-dollar programs, that’s an unacceptable risk.
Key Technologies Shaping the BI Landscape
Enterprise BI ecosystems are built from several interdependent technologies. While each has a distinct role, together they enable a complete business intelligence capability that transforms data into actionable insights.
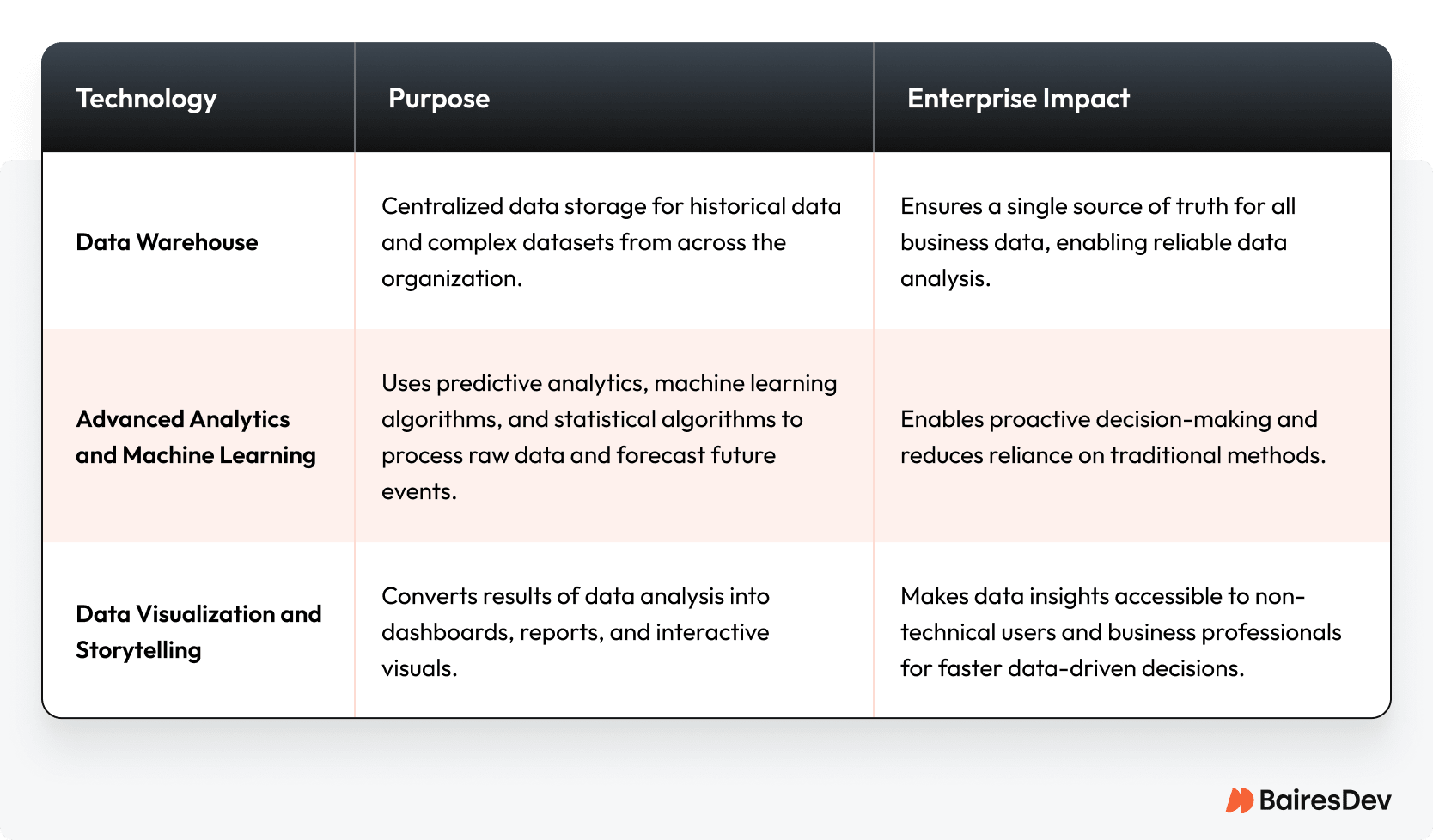
These core technologies are the building blocks that keep enterprise BI running smoothly. But the real impact comes when they grow beyond just supporting specialists. More and more, companies are putting these tools directly in the hands of everyday users—making it easier for everyone to access data and uncover insights quickly. This shift is turning BI from a behind-the-scenes function into a powerful driver of smarter, faster decisions across the entire business.
The Self-Service and Augmented Analytics Revolution
One of the most significant business intelligence trends in recent years is the rise of self-service BI. For large organizations, the bottleneck has traditionally been the data team—business professionals needed to submit requests for every new view or report.
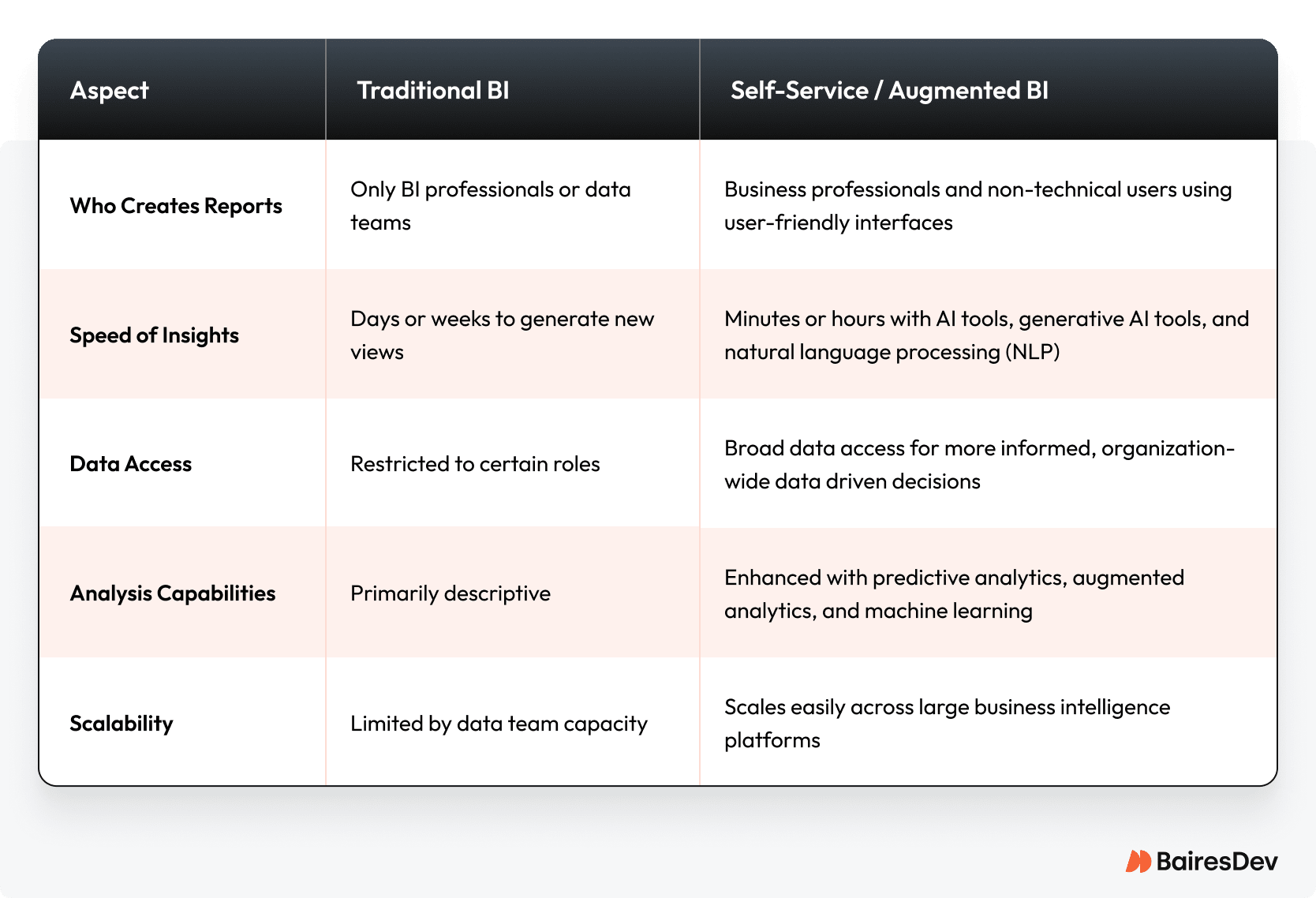
Now, self-service analytics platforms with user-friendly interfaces allow non-technical users to create reports, explore data points, and ask questions in human language—thanks to natural language processing (NLP) and generative AI. Instead of waiting days for analysis, decision-makers can get data insights in minutes.
Augmented analytics takes this further by automating large parts of the analysis process. AI can prepare data, detect anomalies, and even surface unexpected patterns without being explicitly asked.
This shift has three major benefits:
- Faster execution. Decision cycles are shortened across the business.
- Broader access to data. Insights reach more stakeholders, not just specialists.
- Better strategic alignment. Decisions reflect the most current, complete information.
Emerging Trends Enterprise Leaders Can’t Ignore
The business intelligence landscape is evolving quickly, and several new trends will have a direct impact on data-driven decision-making in large organizations over the next few years.
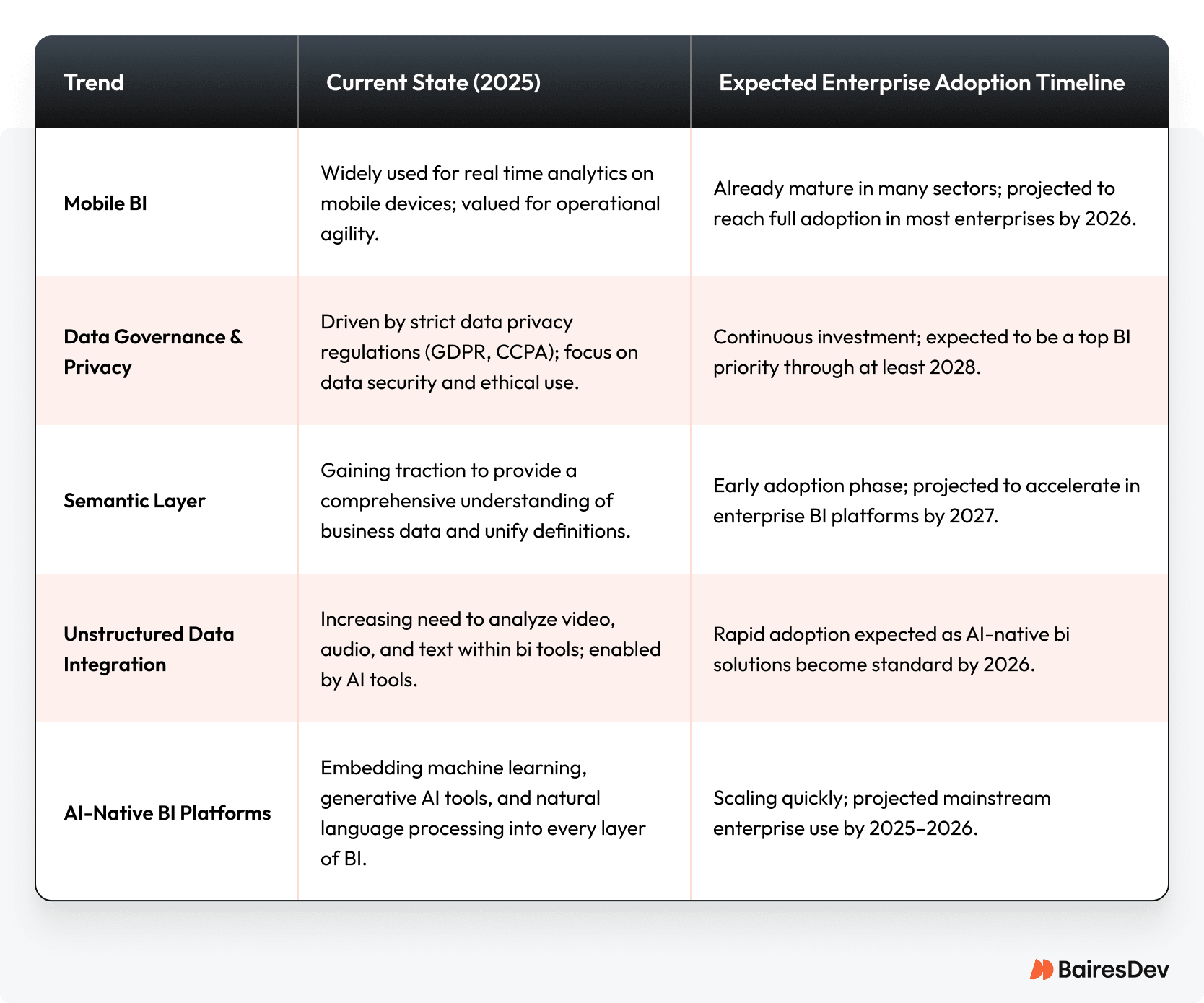
As these emerging trends gain traction, they will fundamentally reshape how enterprises approach data-driven decision making. These innovations expand the reach of BI while also deepening its impact.
From Data to Delivery: BI’s Real Strategic Value
When implemented well, BI becomes an operational advantage. In 2023, organizations that fully invested in data governance outperformed their peers financially by approximately 20%, showing that BI’s value often lies in governance, not just technology.
The ability to integrate business analytics into daily decision-making affects multiple layers of enterprise performance:
- Product delivery. Predictive analytics can flag likely schedule risks weeks in advance, enabling resource adjustments before deadlines slip.
- Market responsiveness. Real time analytics help leadership respond to competitor moves or shifts in customer behavior without waiting for the next quarterly review.
- Operational efficiency. Continuous monitoring surfaces inefficiencies—whether in engineering workflows or customer onboarding—that directly impact the bottom line.
This is why leading enterprises treat BI as a strategic asset, not a standalone tool. Business intelligence tools align strategic decisions with data, ensuring leaders act with confidence backed by facts.
Beyond the Dashboard: Securing Your Competitive Edge
The organizations that extract the most value from BI do three things differently:
- Invest in data quality early—eliminating flawed data before it influences key choices.
- Empower teams at all levels—making valuable insights accessible to everyone who needs them.
- Tie BI to measurable outcomes—linking data insights directly to revenue growth, cost savings, or time-to-market improvements.
In an enterprise environment where engineering capacity is already stretched, BI can take pressure off overextended teams by enabling faster, better-aligned decisions—without adding to headcount.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can BI initiatives fail in large enterprises, and how can leaders avoid these pitfalls?
Common failure points include weak data governance, siloed systems, and underestimating adoption challenges. Success depends on early investment in high quality data, strong cross-team alignment, and executive sponsorship.
What’s the ROI timeline for modern BI deployments?
In most enterprise settings, leaders can expect measurable ROI within 6–12 months, often sooner when BI replaces manual reporting processes. Gains come from faster cycle times, reduced decision risk, and better resource allocation.
How do BI platforms integrate with legacy ERP and CRM systems?
Modern BI solutions use ETL pipelines and APIs to connect with legacy platforms, bringing historical data and live transactional data into a unified data warehouse.
What governance frameworks ensure adoption without compromising compliance?
A mix of role-based access controls, audit logging, and data privacy compliance checks ensures data access without sacrificing security.
When should BI be managed internally vs. outsourced?
If your organization has the engineers and data scientists needed to maintain the platform, in-house can work. For faster ramp-up or specialized expertise—especially in regulated industries—outsourcing can reduce risk.
How can BI help overextended engineering teams?
BI automates many data processing tasks, freeing engineers to focus on delivery rather than report building. It also gives leaders informed decisions faster, reducing rework.
What role does BI play in managing unstructured data?
Modern BI tools integrate with AI-powered processors that can analyze text, images, and video, enabling deeper insights from sources once considered too messy to quantify.
What KPIs indicate a successful BI implementation?
Adoption rate, decision cycle time, accuracy of forecasts, and percentage of operational decisions backed by data are key indicators.
How does BI maturity evolve over time?
Organizations move from descriptive reporting to diagnostic analysis, then to predictive and prescriptive insights. Augmented analytics accelerates this maturity curve.
What’s next for BI after deployment?
Continuous optimization—expanding data access, incorporating trends like AI-native BI, and tying insights to evolving business strategies.





